Sprockets can be classified into normal sprockets, HK sprockets as well as other sprockets.
1. Standard sprocket
Common sprockets are ANSI sprockets which can be engaged with typical series roller chains. See P125 for dimensions.
You will discover two kinds of tooth profiles: U-tooth and S-tooth.
2. HK sprocket
HK sprockets might be engaged with HK series roller chains, and these for single strand chains are identical to standard sprockets. Nonetheless, sprockets for a number of strand chains are various from regular sprockets in sprocket tooth profile.
3. Other sprockets
Other sprockets are designed in accordance on the following calculation formulas to suit respective specialty chains.
The sprockets made use of for your following chains will be the identical since the regular sprockets in tooth gap type, but various in tooth thickness (sprocket tooth profile).
4. Calculation of sprocket dimensions
The dimensions of standard sprockets along with other common sprockets are calculated as follows. At the outset, the diameters of sprockets are calculated from your following calculation formulas.
Following, sprocket tooth profile (the form with the tooth depending on its thickness) is calculated in the following calculation formulas. (The values shown from the following pages have been calculated by these formulas and thought to be the normal values.)
Calculation formulas for diameters and tooth gap forms Calculation formulas for diameters
Calculation of pitch diameter, tip diameter and caliper diameter
The fundamental dimensions of the sprocket appropriate for any chain pitch of 1 mm are respectively known as pitch diameter factor, tip diameter issue and caliper diameter element. The respective variables for respective numbers of teeth are listed beneath. If these variables are multiplied by chain pitch, the basic dimensions from the corresponding sprocket may be obtained.
Illustration:
Inside the case of 80 (25.40 mm pitch) with 35 teeth Pitch diameter (Dp) 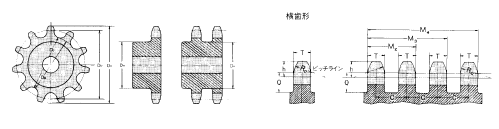
Calculation formulas for tooth gap kinds
Because the most rational tooth gap varieties by which the pressure angle alterations in response on the elongation of a smoothly rotated roller chain together with the lapse of services time, ANSI specify two varieties of tooth profiles: U-type and S-type. On the whole, S-type tooth profiles are adopted in accordance with ANSI, and our conventional sprockets also have S-tooth profiles.